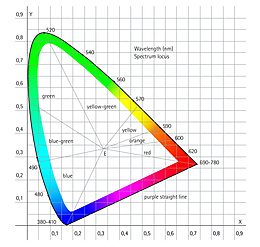
Electronic control units allow individual light colors or the color temperature (tunable white) to be modified. In this way, discreet but also very effective color creations and changes can be achieved, and the perception of color in works of art can be influenced. This is particularly advantageous in rooms where the uses frequently change: museums and galleries for example can flexibly adapt their lighting to the respective exhibition via additive color mixing, thus gaining further display options.
In Human Centric Lighting (HCL) applications, a color temperature adapted to the time of day is also relevant for the well-being of people. Ideally, the lighting concept should take into account the circadian rhythm, i.e. the ‘inner clock’ of human beings, and create a dynamic adaptation of the course of daylight.