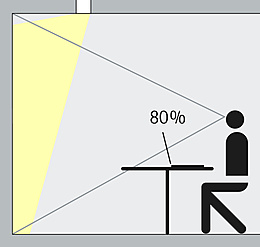
The debate concerning attractive, creatively stimulating and flexible office worlds is in full swing but a considerable part of office equipment is still observed quantitatively—the lighting. Although light is of essential importance in knowledge-orientated work environments that focus on people: light can significantly contribute to the quality of the room and support dialogue and concentration. We show you what lighting concepts look like that meet the needs of a dynamic, digitally networked knowledge society.
Other topics
Contact
Contact
myERCO
myERCO
Your free myERCO account allows you to mark items, create product lists for your projects and request quotes. You also have continuous access to all ERCO media in the download area.
LoginDownloads
Downloads
Technical environment
Technical environment
Standard for USA/Canada 120V/60Hz, 277V/60Hz
- 中文
- 日本語
- 한국어
Our contents are shown to you in English. Product data is displayed for a technical region using USA/Canada 120V/60Hz, 277V/50Hz-60Hz.
More user friendliness for you
ERCO wants to offer you the best possible service. This website stores cookies for this purpose. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies. For more information, please read our privacy policy. If you click on "Do not agree", essential cookies will continue to be set. Certain contents of external pages can no longer be displayed.
{{ tu_banner_headline }}
tu_banner_copy